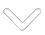Empower your team with a fully automatic and future-proof helium-3-free system
100 mK - 300 K
< 3 hours
300 mK

Key benefits
Speed up your development cycles with the fastest cryogenic characterization device on the market
Fast sample characterization
With the L-Type Rapid’s sample exchange mechanism you can prepare your sample outside the cryostat on a ‘Puck’ and load it in just a couple of minutes (there is no need to warm up the cryostat). After the low-temperature test is completed, samples can be removed easily, and within a few minutes the next sample, prepared on a spare Puck, can be loaded.
The entire process from installation and cooling to the base temperature takes less than three hours, therefore enabling high-throughput screening of scientific samples and rapid prototyping of quantum electronics.
Wide temperature range
ADR systems are equipped with a heat switch to decouple the solid-state cooling medium from its pre-cooling stage during the demagnetization refrigeration process.
In the L-Type Rapid, the latter supports continuous operation at 300 mK and one-shot cooling down to 100 mK. The weak thermal link provided by the heat switch also enables heater-assisted continuous temperature sweeps from base to room temperature.
In contrast to typical He-based refrigerators, the L-Type Rapid offers simple access to a large temperature range, making additional equipment or accessories for working with very low temperatures obsolete.
Highly modular cooling platform
Take advantage of the versatility of a modular product by configuring the device for your specific use case.
Options include the integration of high-quality electronics in a variety of configurations, magnetic shielding, a 5 T sample magnet, Quantum Machines’ cryogenic control systems, and a large Puck 55.
Options and components
Wiring and cryo-electronics
standard DC lines can be extended with several radio frequency lines equipped with multiple RF electronic components such as amplifiers, isolators, and low-pass filters used for the characterization of quantum devices
Magnetic shielding
to investigate and operate sensitive superconducting samples and quantum devices
5 Tesla sample magnet
smooth bipolar operation to study magnetic properties
Enhanced compatibility
compatible with Quantum Machines’ cryogenic control systems offering optimized interfaces and connectivity for sensitive quantum devices
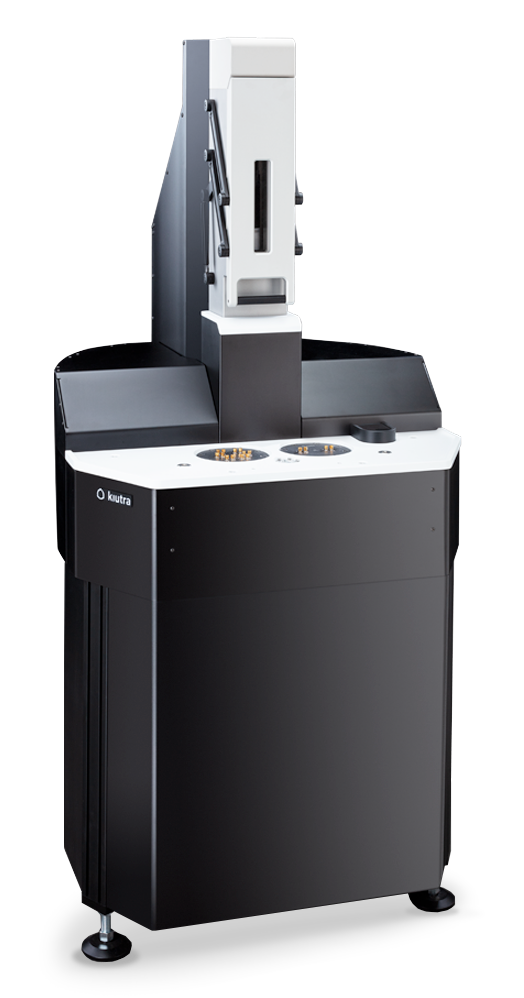
Sample Puck 55
more space, lines and flexibility for your investigations of quantum devices and material samples
Our customers
We are trusted by leading companies and research institutions around the world

Jens Repp
System Engineer Trapped Ion Quantum Computing at Infineon Technologies AG
“It is a great experience to work with the L-Type Rapid, really plug and play and we could do measurements from day one. And the Cryogenics as a Service helped us to bridge the time before the delivery and accelerate our cryo-CMOS developments. Looking forward to characterize our cryogenic control electronics for our ion traps with the new cryostat.”
Sample loading video
Discover the fast and convenient the loading process
Performance data
Fast and hassle-free operation
Fast sample cooldown
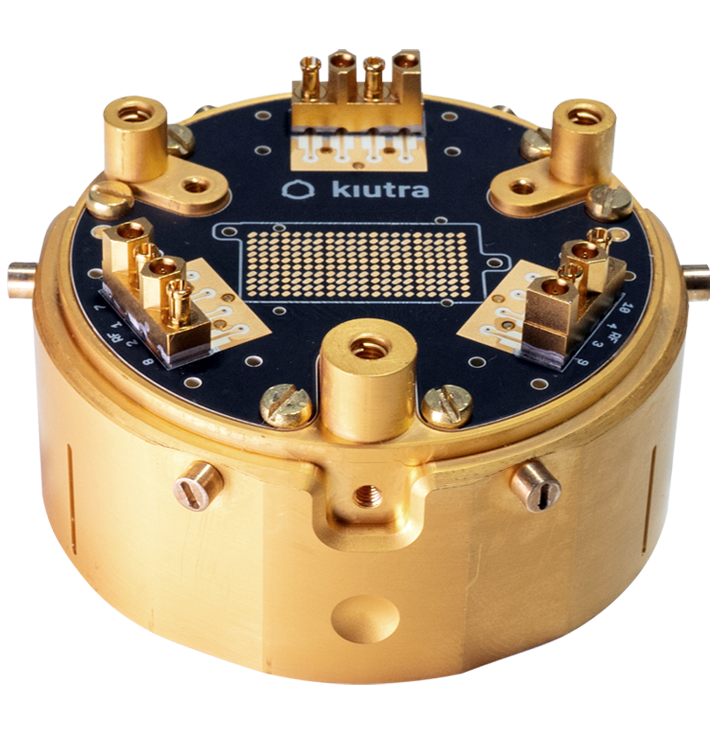
The cumbersome and time-consuming operation of large and complex refrigerators is a bottleneck in the development of novel functional materials as well as next-generation quantum devices. The L-Type Rapid, with its puck-based sample loader, offers a fast and automatic sample cooldown, increasing sample throughput and accelerating the screening of material samples and quantum devices.
The figure shows a typical time-temperature curve for our sample puck with a test device mounted, while cooling from room temperature to sub-Kelvin temperatures. In the initial 1.5 hours, the puck is cooled to the cryocooler base temperature. After the puck is fully thermalized, the ADR cooling units can be charged. This process takes approximately 1 hour. Subsequently the demagnetization cooling is started, and the system can be operated either continuously at temperatures as low as 300 mK, or at 100 mK for a limited hold time.
Apart from mounting the puck in the vacuum lock, the operation is automatic and can be controlled through a modern and intuitive instrument control software.
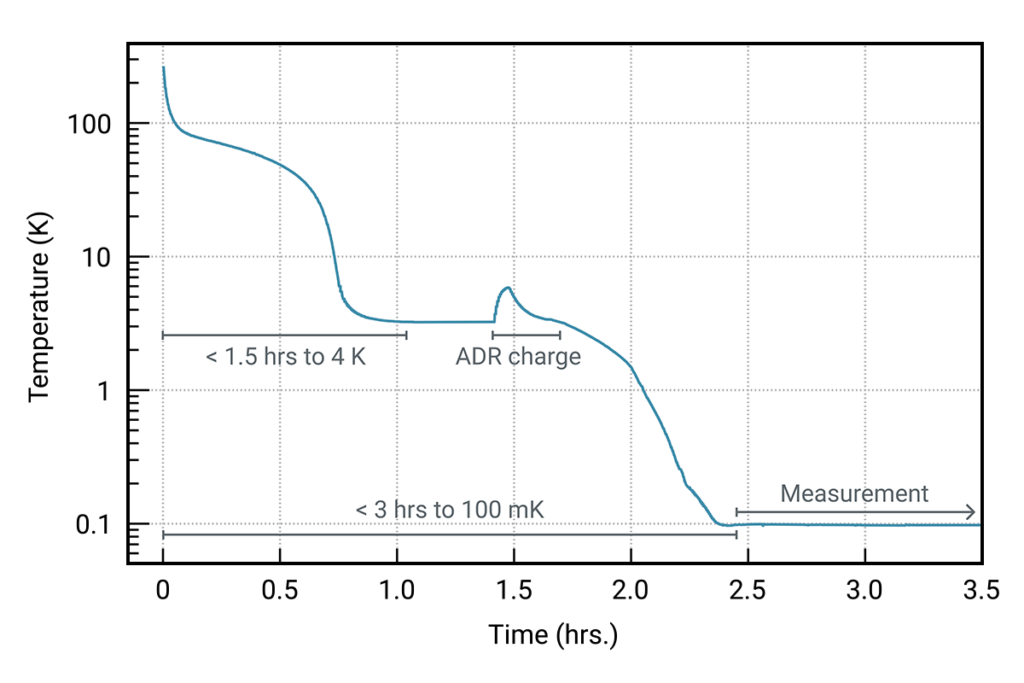
Continuous operation at 300 mK
Conventional adiabatic demagnetization refrigerators (ADR) allow only for “one-shot” cooling. By combining multiple ADR units, kiutra’s cryostats can provide both “one-shot” and additionally continuous sub-Kelvin cooling (cADR) independent of the supply with cryogens.
In its standard configuration, the L-Type Rapid uses two ADR units to generate continuous cooling. The figure shows the temperatures of both ADR units running in cADR mode at 300 mK. While the first unit cycles between the 4 K main heat bath (provided by the cryocooler) and a temperature below the target temperature, the second unit controls the sample temperature. As a result, the sample stage can maintain a constant temperature of 300 mK with a typical temperature stability <0.1 %, and a slightly reduced stability <2 % when activating its heat switch to initialize the regeneration.
Specs
| System size (cm) (w x l x h) | cryostat (sample changer open) rack compressor | 94 x 94 x 232 60 x 80 x178 45 x 53 x 63 |
| System weight (kg) | cryostat | < 600 |
| Residual field at sample stage (mT) | < 0.05 (0.5 Gauss, 50 µT) | |
| Vibration (µm) | < 10 µm | |
| Size of Sample Puck (mm) | diameter | ø 36 |
| Sample cooldown time (hours) | 300 K – 4K 4 K – 0.1 K total 300 K – 100 mK | < 1.5 1.5 < 3 |
| Cooldown time (hours) | cryostat | < 42 |
| Temperature range (K) | 0.1 – 300 | |
| Continuous temperature control (K) | 0.3 – 300 | |
| Cooling power (µW) | @500 mK @ 1K | 50 160 |
| Operation time (hours) | @100 mK @200 mK | 3 5 |
| Temperature stability | typical while switching stages | < 0.1 % or <0.5 mK < 2 % |
Scope of supply
Cryostat
Sumitomo RP-082B2 closed-cyle pulsetube cryocooler, 1W 4.2K, 40 W @ 45 K
Sumitomo F70H water-cooled indoor helium compressor, 20 m flexlines
Two ADR units for one-shot and continuous operation:
- 2 ADR magnets
- 2 heat switches
- 2 cooling media
Wide range pressure gauge
Integrated passive quench protection
User ports for custom integration:
- 2 x ISO-F 100
- 1 x ISO-KF 25
Instrument control
Custom 19” electronics rack
kiutra Modular Control Unit (MCU):
- Base module
- Power module
- Drive module
- 2x load module
- Gas Handling module
kiutra Compressor Control Unit (CCU)
Temperature monitor
Temperature controller
Calibrated temperature sensor on sample stage
Temperature sensors on cryocooler cold stages and first ADR unit
Sample heater and warm-up heater
User PC with pre-configuration Python-based instrument control software and high-definition display
2x digital high frequency magnet power supply
User breakout
Filtered temperature sensor breakout

Standard wiring
40 DC wires
Gas handling
Pumping, purging and venting of cryostat and Sample Changer airlock chamber
Oil-free roughing pump
Turbomolecular pump
Sample changer
Airlock chamber with motorized sample transfer
Sample Puck Transfer Cage
Additional pressure gauge
1 Sample Puck
1 Sample Puck Testing Station
ISO-F 100 gate valve
Typical applications
Innovative cooling for state-of-the-art science and technology
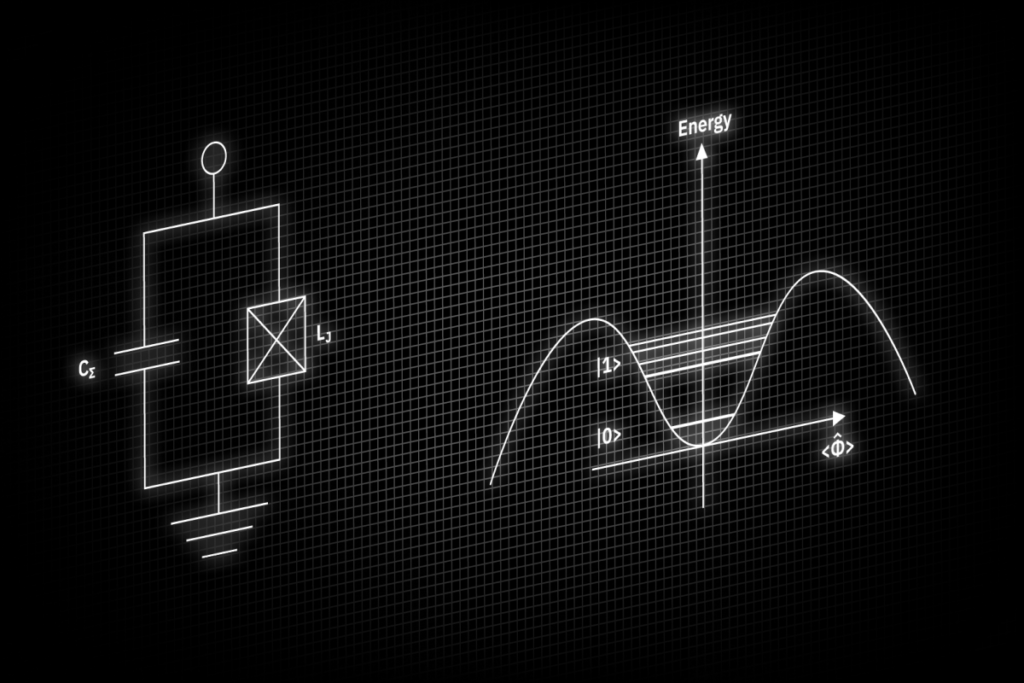
Qubits
With first concepts dating back to the 1980s, superconducting circuits are today one of the most promising technologies in the race to build a universal quantum computer. The key element in superconducting quantum circuits is the Josephson junction – a non-linear element that connects two superconducting islands by a weak link, which can be either an insulating or a metallic barrier. Superconducting quantum circuits offer individual control and readout, and their properties can be engineered by circuit design. During the past two decades, superconducting qubits experienced a rapid improvement of their coherence properties, resulting in the demonstration of several major milestones toward scalable quantum computing. To screen and characterize superconducting thin films and devices more efficiently, kiutra’s L-Type Rapid offers an extremely fast sample cooldown, combined with a large temperature range, and a base temperature as low as 100 mK.
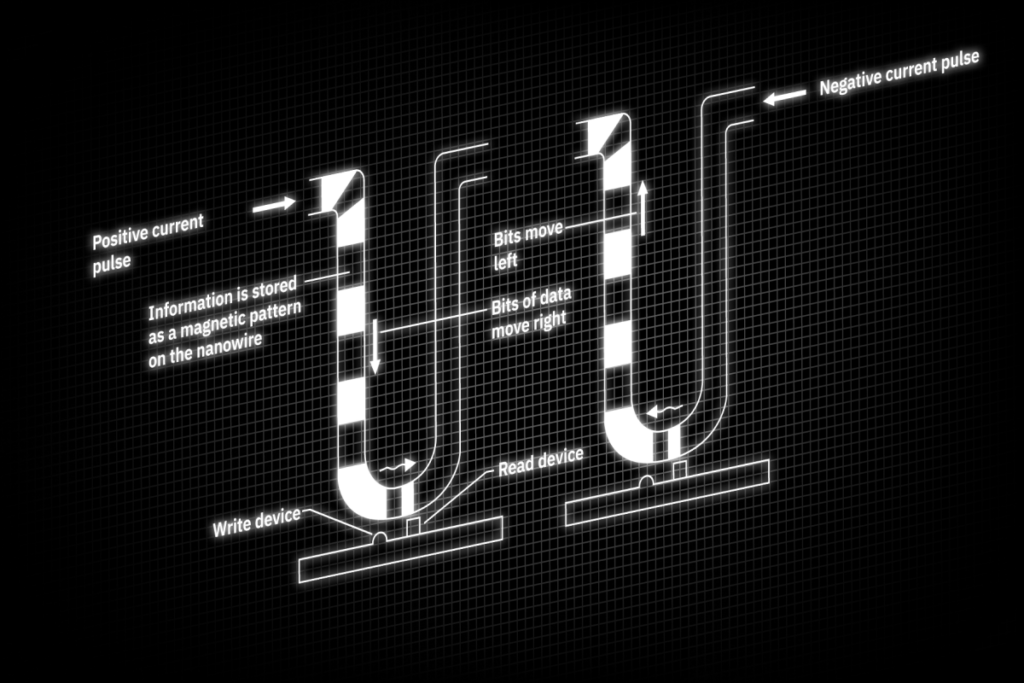
Spintronic Devices
Researchers in the field of spintronics study and exploit the spin-charge coupling in metallic systems. Making use not only of the charge carriers’ charge but also of their spin allows, e.g., to build novel devices like racetrack memory or MRAM to save digital data. These technologies promise low-energy information storage, high reliability, performance, and capacity also at room temperature. However, to better understand the underlying physics and to develop novel materials for spintronic devices, low temperatures, high-frequency cabling, and magnetic field control at the sample position are required. The L-Type Rapid offers access to a wide temperature range from 100 mK to room temperature in a single, cryogen-free, and easy-to-use instrument. Optional upgrades such as a sample magnet, and additional RF and DC wiring allow to implement various experimental setups and low-temperature measurements.